Sound Design Pack's Wave Player Modules with Embedded Examples
This application note describes the Wave Player modules under Sound Design Module Pack in Audio Weaver and demonstrates its embedded uses.
RAM vs FFS vs Flash Players
The first step here would be to understand the fundamental differences between each Wave Player types.
Wave Player RAM 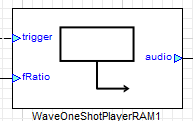 | Wave Player FFS 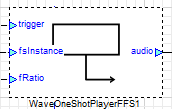 | Wave Player Flash 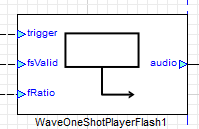 | |
|---|---|---|---|
Basic Workings | Reads the audio samples embedded within the module’s buffer array (AWE heap) | Reads the audio data from samples stored in the AWE flash file system as file (.bin) in RAM | Reads the audio data from samples stored in the AWE flash file system on the target flash device |
Ease of Use | Highly easy to use and usually used in the initial phases of implementation | Moderate difficulty, on embedded targets BSP support is required. | Moderate difficulty, on embedded targets BSP support is required. |
Runtime Wav Filename Exchange | No, runtime wav file exchange is not possible for this flavor of the wave player | Yes, runtime wav file exchange is possible. | Yes, runtime wav file exchange is possible. |
Memory Consumption | Highest Memory consumption of them all. Bloated AWS/AWB | Low memory footprint. | Low memory footprint. |
Usability in Native Mode | Easily useable as is in Native Mode. | Requires additional SND modules like FFSWrapper module and complex to run on native mode. | File operations are used in Native Mode. File path is added in Designer via |
Wave File Dependencies | Requires larger heap size | Needs extra module like FFS Player Module for providing instance pointer to the Wave Players and Audio File Generator* | Has a dependency on AWE Flash File Manager to flash wave or bin files. |
BSP Integration Dependencies | Audio samples are embedded within the AWB. | AWE Flash File System requires the | Depends on direct accessibility of Flash by AWE instance. |
One-Shot vs Loop Player
All of the Wave Player variants come with two subdivision of the playback output types namely One Shot and Loop players which will be discussed in the document below.
One-Shot | Loop | |
|---|---|---|
Basic Workings | Playback continues until the end of the file is reached and then it stops. | This module outputs wave data in loop mode. |
Trigger Based | Playback starts after a low to high trigger edge is received on the ‘trigger’ pin. | Playback starts as soon as the module is enabled. 1 - Enable and 0 - Disable. |
Pitch Shifting Capabilities | Yes | Yes |
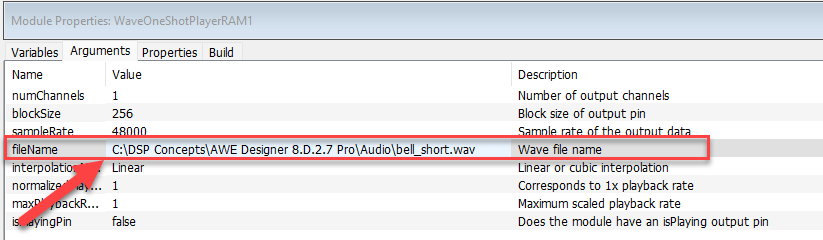
Wave Player - RAM
The RAM based wav player modules basically read the audio samples embedded within the module’s buffer array (Audio Weaver Heap). While connected to an Audio Weaver Server they generally show up in the Slow Heap section. The wave file name along with the path is specified in the Wave Player RAM.
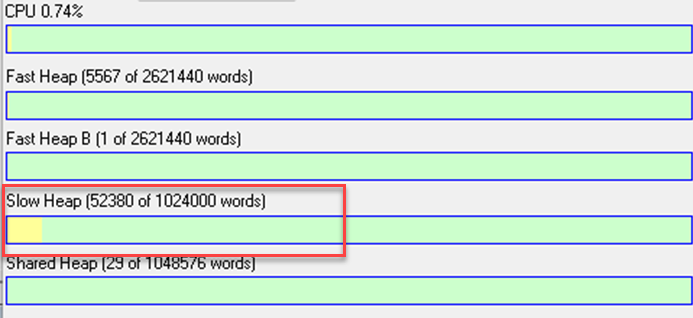
Embedded Example
In this section we will look at a RAM based example on a target hardware. For this example we are using SHARC 21569 with EV-SOMCRR-EZKIT. We will be using this target hardware throughout this Application Note to maintain consistency. For more details about the board please visit EV-21569-EZKIT Website
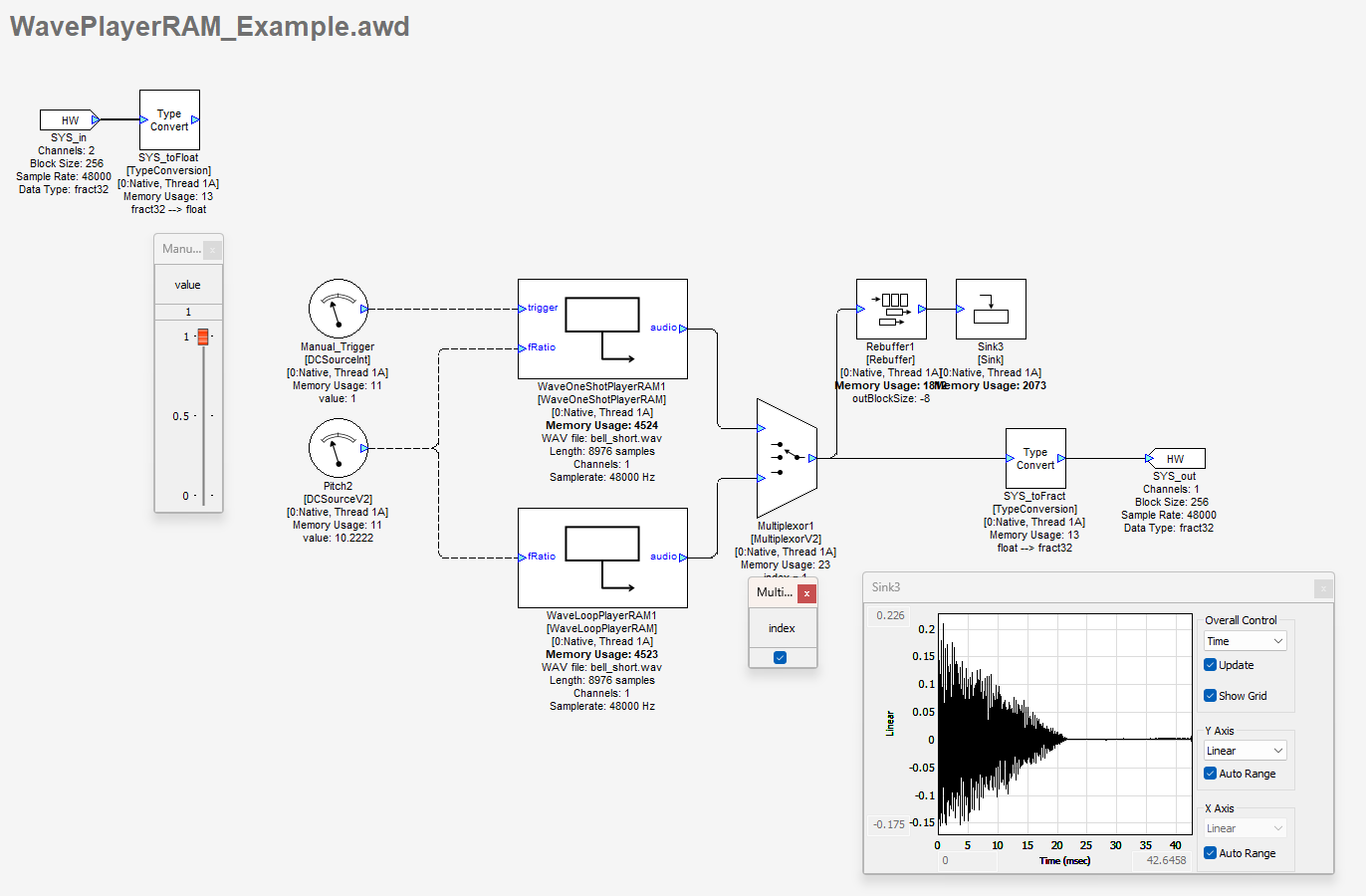
In this example, we are using two Wave Players namely WaveOneShotPlayerRAM and WaveLoopPlayerRAM, to switch between the two wave players we are using a Multiplexor module. The two wave files used in this example are the bell_short.wav and turn-signal.wav. By deselecting the Multiplexor module, the WaveOneShotPlayerRAM path is selected. The trigger for this module requires a a rising edge (0 → 1). Playback continues until the end of the file is reached and then it stops. Retrigger while being in the middle of the playback has no effect and will be ignored. The filename in RAM based players cannot be changed during runtime and will continue with the wave file initially inserted. The wave file is transferred into the Wave RAM player’s file buffer which in turn bloats the awb for the target platform.
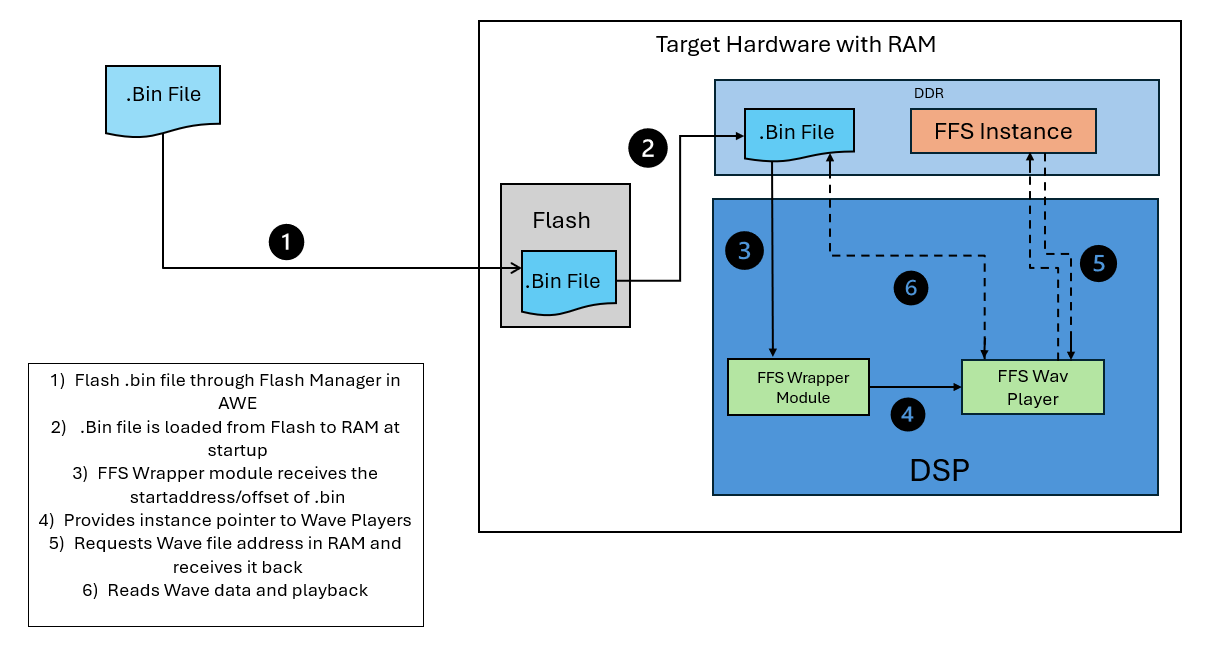
Wave Player - FFS
Basic workings of Wave FFS Players
The FFS-based Wave Players utilize an emulated AWE Flash File System to access and stream wave sample data. These players operate by interfacing with a structured flash file system image that encapsulates a collection of audio assets, collectively referred to as audio libraries.
Within this system, the filename variable in the module acts as a key identifier, specifying the target audio file to be located and parsed within the flash file system. After retrieval, the wave player processes and streams the wave sample in real-time, ensuring efficient playback directly from the RAM without requiring intermediate extraction. This approach optimizes memory usage and reduces latency, making it suitable for embedded or resource-constrained environments.
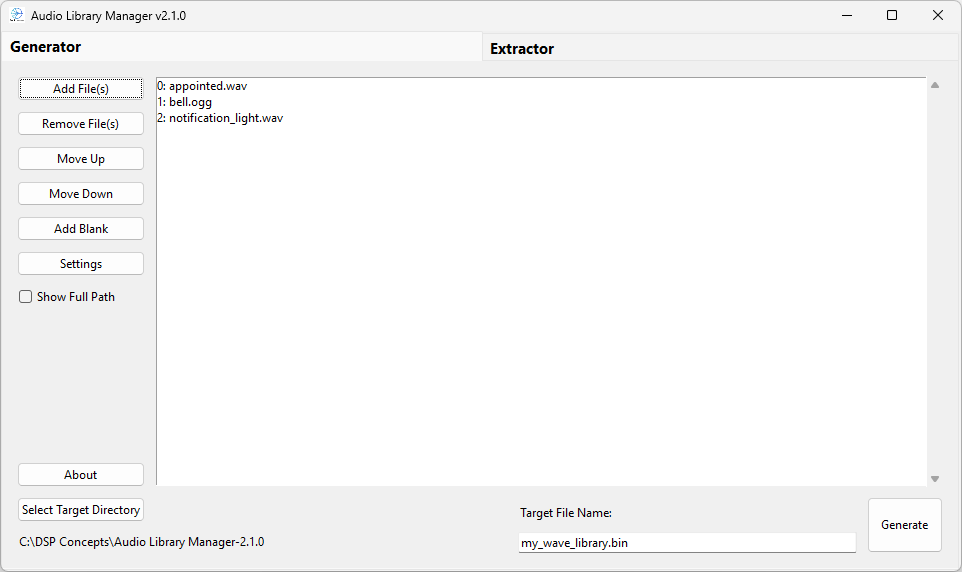
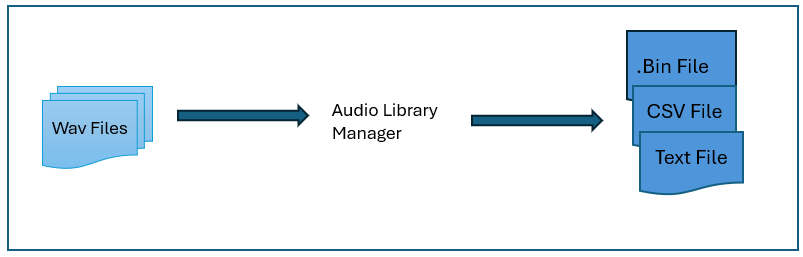
Audio Library Manager Application
The Binary File (Wavelib.bin) is generated by the Audio Library Manager Application previously know as the “WaveLibraryGenerator”. It is an application with a GUI to easily create wave flash file systems that contain audio files to be played on a target hardware or to be tested on a native target. Since it is a standalone app, it is relatively independent of the other software in the sound design module pack. For more details please see documentation on Audio Library Manager
Embedded Example
In this section we will discuss and explain an FFS Example with the same SHARC 21569 EZKit Board as previously used. Please download the Example folder with awd, wav files and binary files required for the example.
FFS_Example.zip
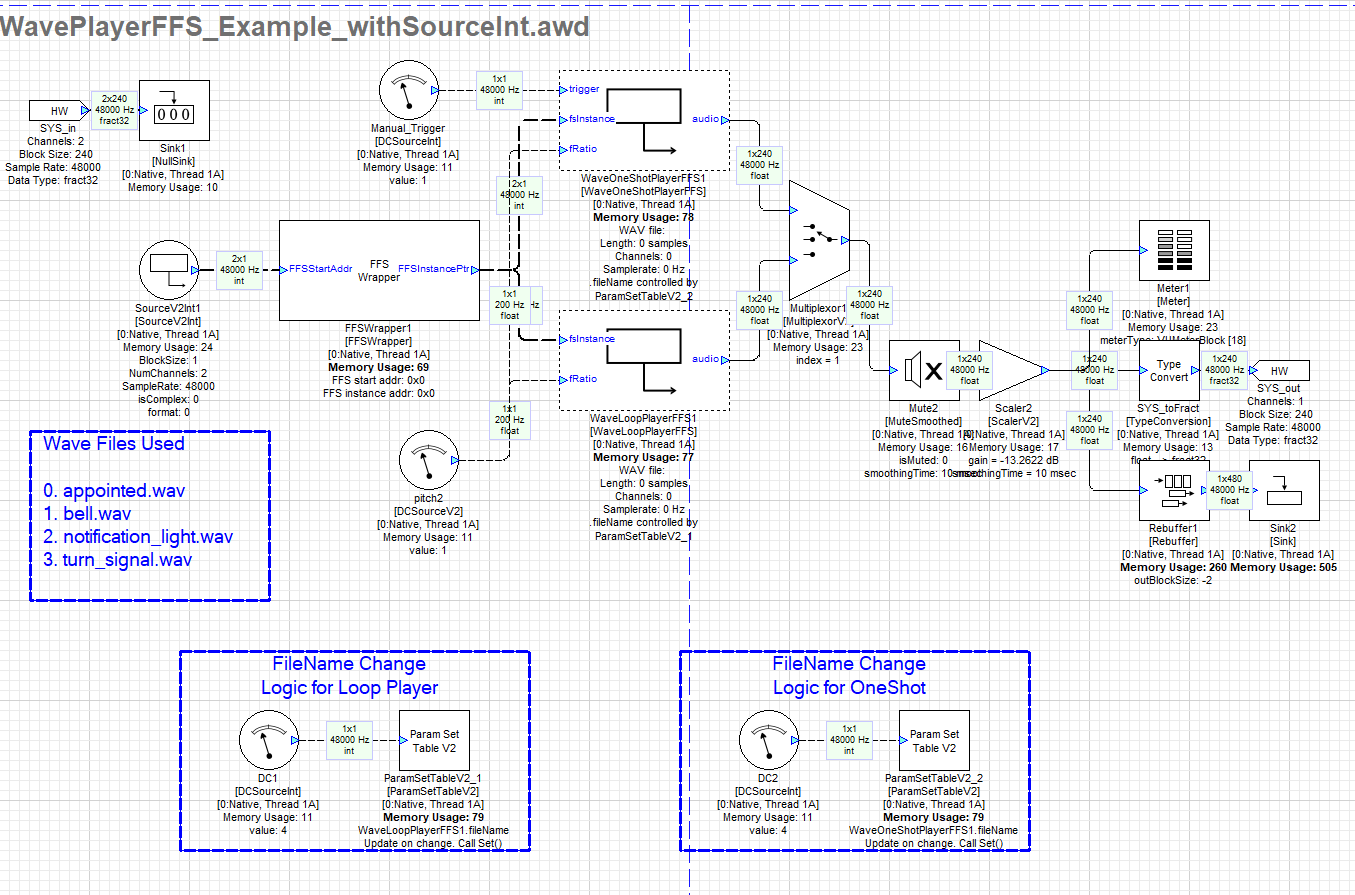
Method 1) Example with FFS Start Address provided through Source Int
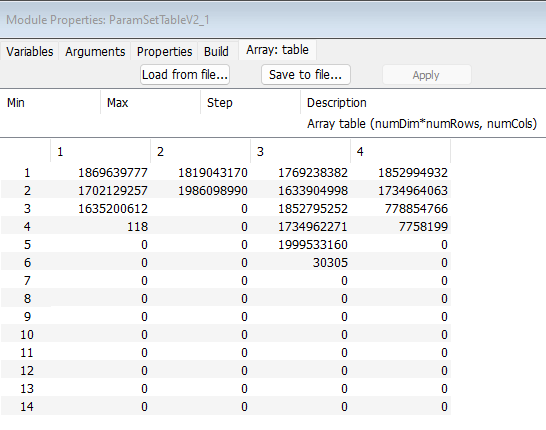
The example below uses a SourceInt to Input the Starting Address of FFS. This is the most common and preferred use case. The DCSourceInt modules is used to select wave files from indexes 0->3. The ‘FFS_wave_library’ csv file contains the audio file names in uint32 format is loaded into the ParamSetTable Module array tab. This is done for both the ParamSetTable modules in this example.
By deselecting the Multiplexor module, the WaveOneShotPlayerFFS path is selected. The Trigger for this module requires a a rising edge (0 → 1). Playback continues until the end of the file is reached and then it stops. Retrigger while being in the middle of the playback has no effect and will be ignored.
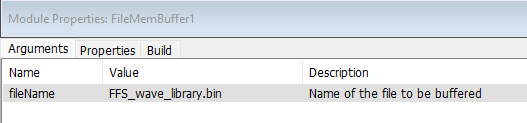
Method 2) Example with FFS Start Address provided through File Mem Buffer Module
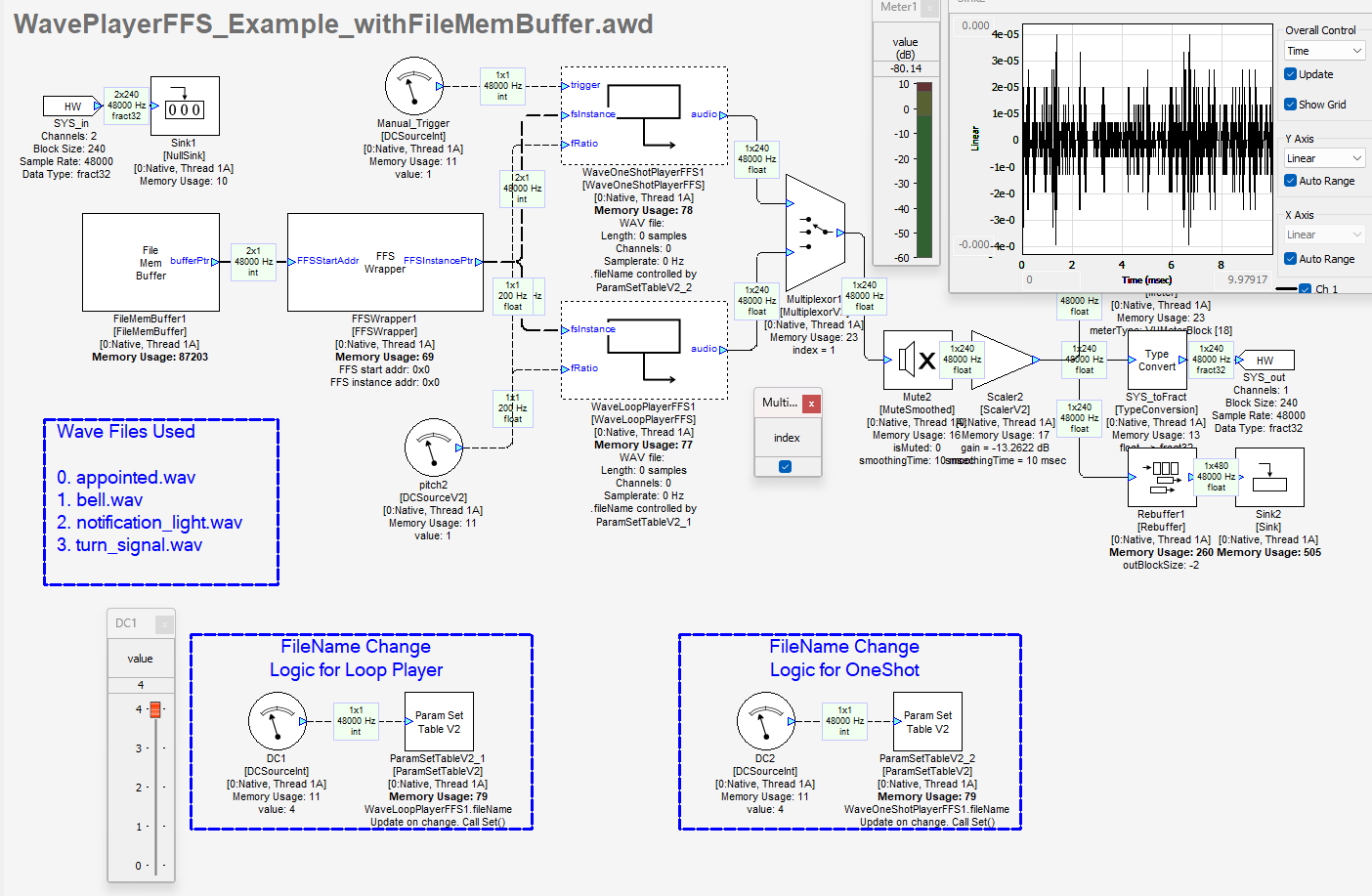
In this example we are using FileMemBuffer from the Sound design module pack to input the FFS_wave_library.bin file in the fileName argument for the FileMemBuffer module as shown in the screenshot below. The path to Binary file is inserted in the Designer File -> File Search Path.
DCSourceInt module is used to select wave files from indexes 0->3. The ‘FFS_wave_library’ csv file contains the audio file names in uint32 format is loaded into the ParamSetTable Module array tab. This is done for both the ParamSetTable modules in this example.

By deselecting the Multiplexor module, the WaveOneShotPlayerFFS path is selected. The Trigger for this module requires a a rising edge (0 → 1). Playback continues until the end of the file is reached and then it stops. Retrigger while being in the middle of the playback has no effect and will be ignored.
The addition of FileMemBuffer module bakes the Binary file into the AWB when the target files are generated.
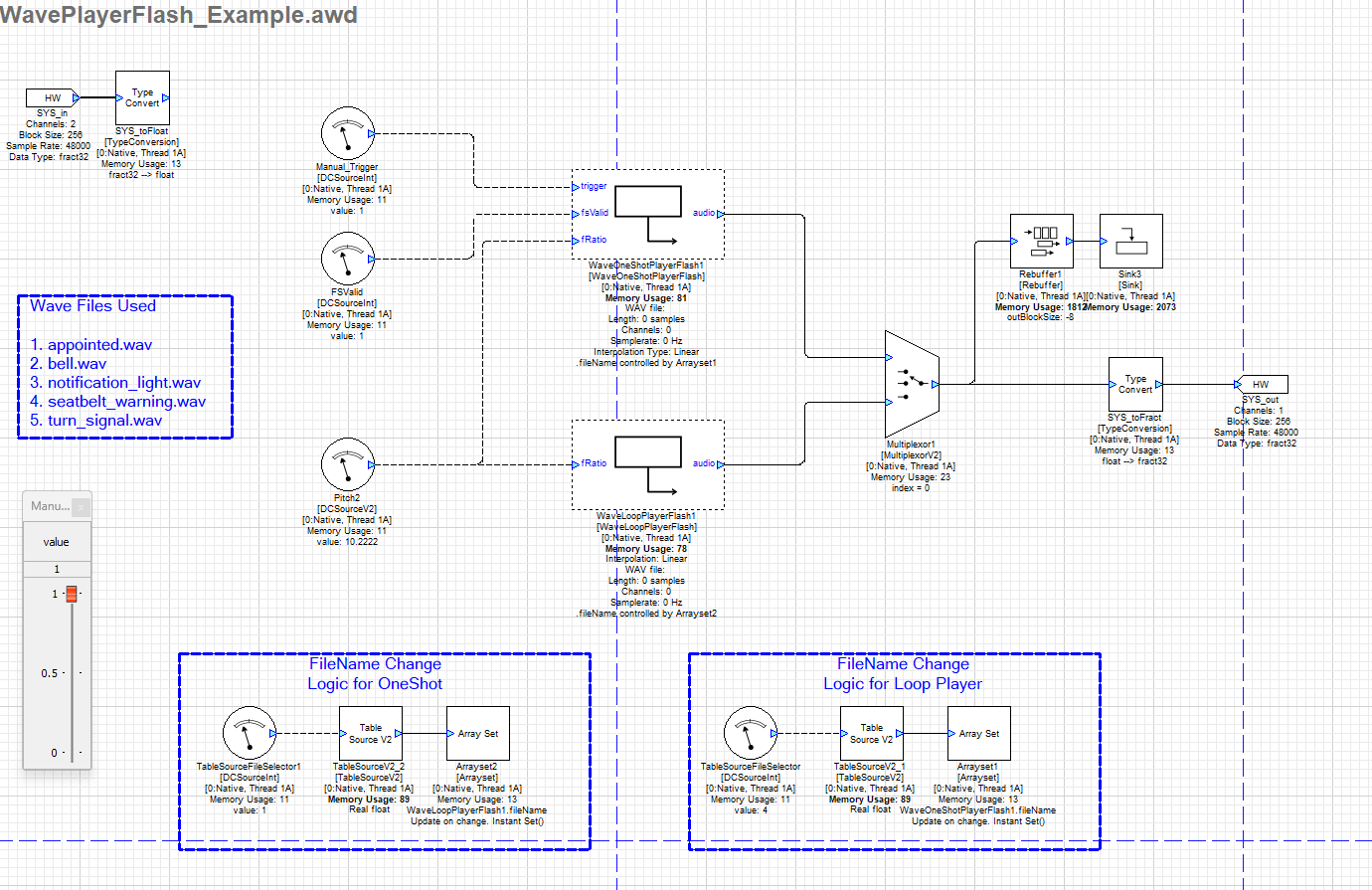
Wave Loop Player - Flash
The Flash-based Wave Player retrieves and processes audio data from pre-stored wave samples residing within the AWE flash file system on the designated target flash storage device. It directly interfaces with the structured flash memory layout, efficiently parsing and streaming audio samples for real-time playback. The system leverages low-level flash memory access mechanisms to optimize read operations, ensuring minimal latency and efficient resource utilization. These modules require an additional input as the fsValid Pin which is Valid when set to '1'.
Embedded Example
In this section we will discuss and explain an Flash Example with the same SHARC 21569 EZKit Board as previously used. Please download the Example folder with awd, Wav files and Bin files required for the example.
Flash_Example.zip
Method 1) Adding the Wave Files directly to the AWE Flash File Manager
In the example shown below we add the selected wave files directly to the Flash Memory on 21569 SOM. The flash memory reserved for this file system may be part of the processor chip itself, an external part or simulated in the target file system. For this AWE Flash Manager is used, the wave files are added to the Flash Manager and flashed onto the target Flash Memory.
After the files are successfully flashed, the Flash Wave Players are able to access the wave files during runtime. In the example below we are using two types of Flash wav players namely OneShot and Loop, while the OneShot is triggered. The output from these Wave modules is switched using the Multiplexor1 module. In this example the fileName argument for the wave players are being set by ArraySet module
Method 2) Adding the Wave Files to a Bin and then flashing via AWE Flash File Manager
Adding Files to the Target Flash File System
Traditionally, files are added to the target Flash File System (FFS) using the Flash Manager within the AWE Server. However, this approach has limitations, as it requires an active connection between the Server and the target, and each file must be manually added.
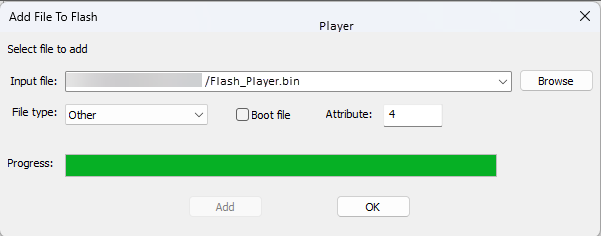
To streamline this process, use the Audio File Manager to generate a Bin file.
The generated Flash_Player.bin file is flashed through the AWE Flash Manager.
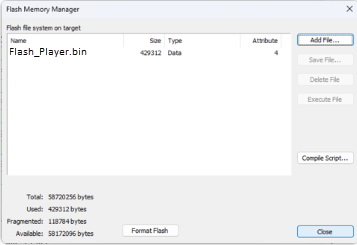
Once the binary file is successfully flashed , the WavePlayerFlash_Example.awd can be run while server is connected to the target.
Common Errors in the SND Modules
Error # -50 → E_FILE_NOT_FOUND
This error can occur in two cases:
a) When the path to the wave file is not reachable or properly defined. Maximum absolute file path should not be more than 512 characters. It can also be due to corrupt Bin file or csv file.
b) When directory entry for file not found (“force stop” is a valid use case!)Error # -51 → E_ILLEGAL_FILE_ATTRIBUTE
Occurs when the wave data sample bit resolution is not 16 bit.Error # -56 → E_ERROR_READING_FLASH_MEMORY
Binary file not found or corrupted.Error# -47 -->E_NO_MORE_FILES
Binary file not found or corrupted.