Subcanvas Array Set
Overview
Sets module array values inside of a Subcanvas.
Discussion
This module is a version of the Subcanvas Param Set that is able to write into array variables inside of a Subcanvas. The name of the Subcanvas module and the name of the internal variable are specified as module arguments. The module writes the array in the real-time thread and you can optionally call the module's Set() function. If the module to control has associated range information, then the Subcanvas Array Set can be configured to clip to the allowable range.
The module will write the input pin values to the target array, and is also flexible enough to specify which portion of the internal array should be written to. That is, the entire array does not need to be written and the size of the input wire does not need to match the array size. See the step and startIndex variable sections for more details.
The target Subcanvas module must be on the same instance as the Subcanvas Array Set module. If they are not on the same instance, there will be an error at build time. While it is not enforced, it is also (highly) recommended to align the clockDivider of the Subcanvas Array Set module and the target module inside the Subcanvas (see the clockDivider field of the target module in the AWC file). Failure to align these could result in updating an array while it is being used in the Subcanvas layout.
The modules uses information from the Subcanvas's JSON file to identify which variables are available to control. The JSON file contains variable names, data types, range information, and array sizes. If the JSON file has range information for the selected variable, then the inspector will provide a checkbox to enable or disable range checking. This checkbox is only there if the module has range information.
There is logic in the module to prevent you from writing out of the array bounds. If you do try to write outside of the array bounds, then the 'Index Out of Bounds' LED will be lit on the inspector and only the values that fall within valid array indices are written.
There is an errorStatus variable that will be set to a negative value if an error has been encountered. errorStatus is included in the module inspector. Common errorStatus values are:
0 (E_SUCCESS): No error encountered.
-26 (E_NO_LAYOUTS): The Subcanvas module does not have a valid layout running (e.g. loadNow variable is set to ‘Empty’).
-82 (E_BAD_MEMBER_INDEX): Combination of step, startIndex, and array and input pin sizes results in writing no values to the target array.
-83 (E_CLASS_NOT_SUPPORTED): The objectHandle points to a module of an unexpected classId.
For other values of errorStatus, see Bin\Assets\module\include\Errors.h for details.
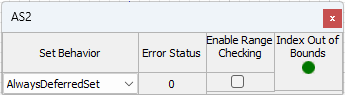
Subcanvas Array Set inspector, with range checking available on target array
This module always supports an optional enable pin.
Arguments
subCanvasName
Points to the Subcanvas module that the target module is in. This can be the path relative to the Subcanvas Array Set module, where '\' is used to go up a level in hierarchy, or it can be the alias name if the Subcanvas module has an objectAlias defined.
modVar
The array variable to write is specified in mod.var format. The array variable is specified as modName.variableName, where modName is the name of the target module as listed in the AWC file associated with the Subcanvas pointed to by subCanvasName. This name will either be the full hierarchical name of the target module, or the alias if it has an objectAlias assigned.
If the variable being written is not an array, then you will get an error when you build the system. If you need to write a scalar variable then use Subcanvas Param Set module.
enablePin
If set to True, this argument creates an enable pin which can be used to enable or disable the writing of the array. This pin accepts integer inputs only of blockSize = channels = 1. Any non-zero value is treated as enabled.
executionOrder
The executionOrder argument enforces the order of processing of the Subcanvas Array Set module relative to the target Subcanvas module. After means that the Subcanvas Array Set module will execute after the target Subcanvas module, and Before means that it will execute before the target Subcanvas module. The default is Undefined, which means that no execution order is enforced.
Note that this argument only functions for the Classic build engine type (see here for more information, including how to accomplish this for Hierarchical builds: https://documentation.dspconcepts.com/awe-designer/latest-version/preferences-and-layout#id-(8.2025.3)PreferencesandLayout-BuildEngine ).
Variables
setBehavior
The write behavior of the module is specified on the inspector in the 'Set Behavior' droplist. The array variable is written on every pump, however the Set function can be configured.
AlwaysNoSet (0) - the module's Set function is never called.
AlwaysDeferredSet (1) - the module's Set function is called from the deferred thread.
AlwaysInstantSet (2) - the module's Set function is called every time from the real-time thread, after the target array has been written. This can lead to an increase in the CPU load.
The default setting is AlwaysDeferredSet.
startIndex
The startIndex variable specifies the position to start writing into the array, and it lets the user update only portions of the target array. This is a zero-based offset, can be positive or negative, and is 0 by default. If it is negative, samples are skipped by increments of ‘step’ until it is positive (call this N), at which point we start writing into the target array. The first N samples of the input wire will not be copied to the target array.
See the Block Overlap Writes section below for details on this behavior.
step
The 'step' variable is added to the target array index after every write occurs. For example, if step=1, then values are written sequentially into the array. If you set step=2, then every second value in the array is written. Note that step only applies to the write index into the array; the read index from the input wire buffer always increments by 1.
See the Block Overlap Writes section below for details on this behavior.
enableRangeCheck
Enables range checking of the input values being written to the target array. The boundary values used for the range from the AWC module for the target module’s array. These come from the ‘Min/Max’ values of the Array tab for that target module’s array. Note that the ‘Step’ value from the Array tab is not honored in the range checking done by this module.
Block Overlap Writes
The startIndex and step variables can be confusing, especially since startIndex can be negative and startIndex + numValues * step can be greater than the size of the target array (or even a negative number!). This flexibility of the startIndex and step, plus the fact that they can change during runtime, makes it possible to do things like write only one channel of data from an array, or update only portions of it at a time. The diagrams below are meant to help understand the block overlap design used to decide which input pin elements get written into which target array elements.
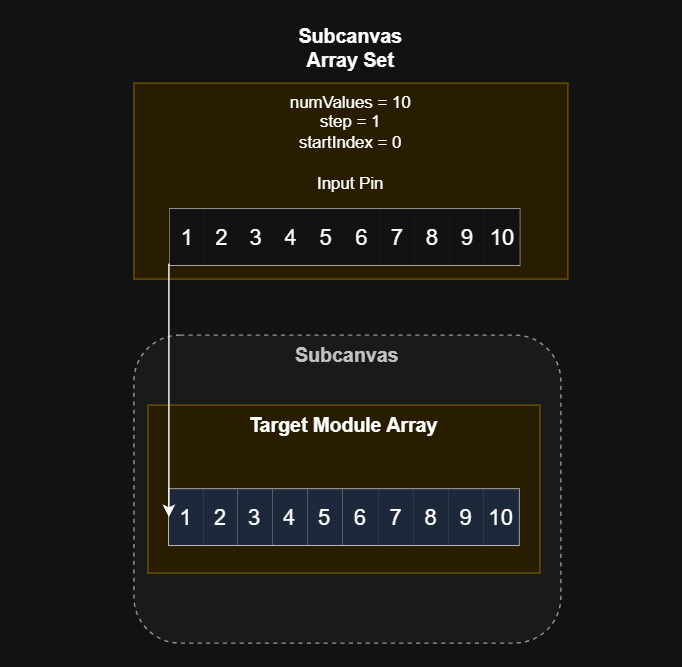
Perfect Overlap
This is the easiest case, and the most common. The target array is the same size as the module input, step == 1, and startIndex == 0. The input pin is simply copied directly to the target array.
Perfect Overlap with Step
In this example, the input pin size is 5, the target array size is 10, and step is 2. startIndex is 0. With a step of 2, every other element of the target array is written to by the first 5 elements of the Subcanvas Array Set input pin. In this case, every even value of the target module array remains unwritten.

This is one way to write to only the first channel of a stereo target array.
Partial Overlap, Positive Start Index
In this case, startIndex is > 0 and step is 1. This means that the overlap between the target array and the module input is smaller than the size of the input pin. The last arraySize - startIndex values of the target array will be equal to the first inputPinSize - startIndex elements of the input pin. The first startIndex values in the target array remain unwritten.
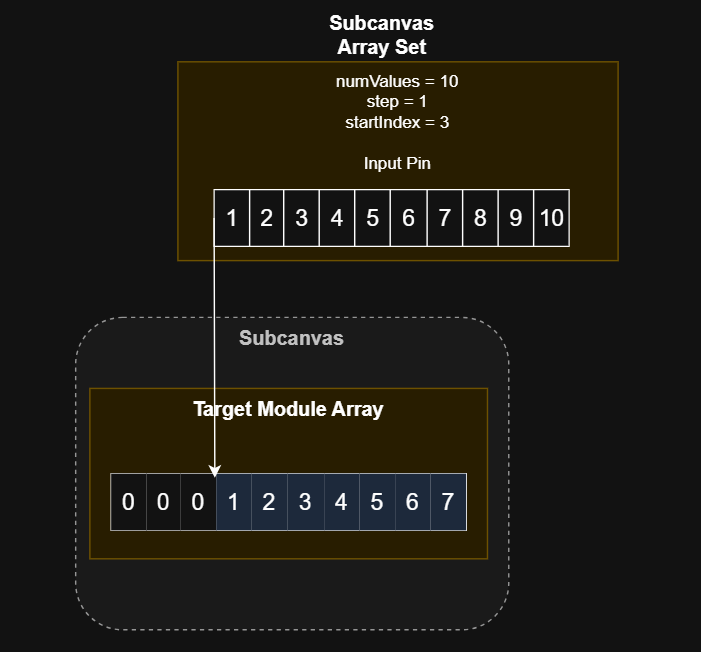
Partial Overlap, Negative Start Index, Non-Unity Step
In this case, startIndex is -5 and step is 2. This again means that the overlap between the target array and the module input is smaller than the size of the input. However, since the overlap covers the left side of the target array, the first startIndex / step values of the input will be ignored. The remaining values will be copied to beginning of the target array, at intervals of 2 until the end of the target array is reached.
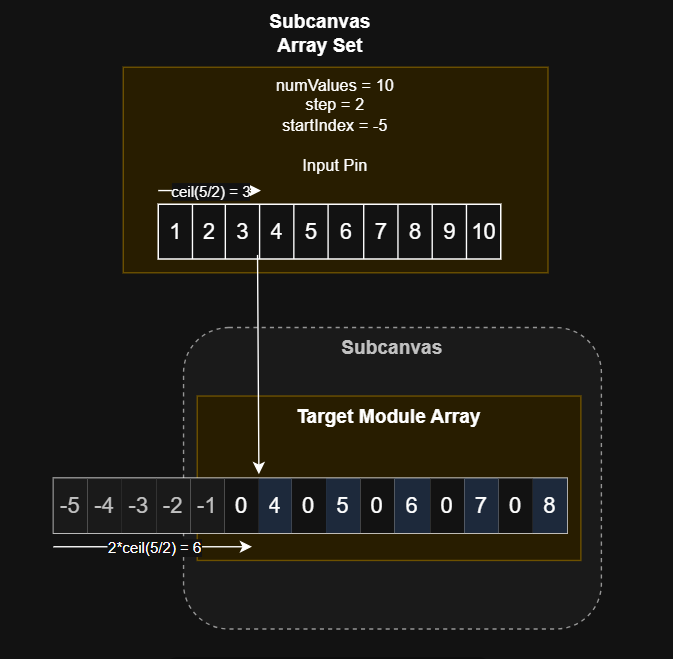
As seen above, the first value that can be written in the target array is calculated as step * ceil(-startIndex/step). In this case, that means that we move forward 6 spaces in the target array, starting at -5. So the first element written to is the second element in the array (array[1] in C syntax). Since step does not apply to the input pin, we skip ceil(5/2)=3 elements in the input pin and begin writing from there. We continue copying every sequential value from the input pin to every other value in the target array until we reach the end of the target array. In this case, the final two values of the input pin are unused.
Deinterleaved / Interleaved Behavior
Wires in Audio Weaver are always assumed to contain interleaved data. However, some module arrays will store data in deinterleaved format, which can lead to unexpected behavior if it is not known when using this module. The most notable such modules for the Subcanvas Array Set are the Buffer Source modules. The original versions always stored the .value array in deinterleaved format - it is recommended that the user always use the Buffer Source V2 modules instead, which introduced the .format variable that determines whether the internal .value array is interleaved or deinterleaved (.format = 0 means deinterleaved, .format = 1 means interleaved). The AWC contains this information, which can be referenced when configuring this module to point to a Source module. The formatting of the Source array will change how step and startIndex should be configured, and also how the data on the input pin must be organized.
Module Pack
Advanced
ClassID
classID = 1451
Type Definition
typedef struct _ModuleSubcanvasArraySet
{
ModuleInstanceDescriptor instance; // Common Audio Weaver module instance structure
INT32 setBehavior; // Controls the set behavior of the module
INT32 startIndex; // Location to start writing into the target array
INT32 step; // Increment between writing of values to target array
INT32 outOfBoundsIndex; // Boolean that indicates when the module is asked to write outside of the array bounds
INT32 enableRangeCheck; // Turns on range checking of values
INT32 errorStatus; // Shows the current status of the module. 0 means no error. See module docs for details
UINT32 objectHandle; // Integer control handle of the internal module to control
UINT32 targetClassId; // Class id of the target module, used for validating access of object
INT32 arrayLength; // Total length of the array variable
UINT32 mask; // Mask value used when calling the set function
INT32 minValue; // Minimum value for range checking. Will be scrambled for float values.
INT32 maxValue; // Maximum value for range checking. Will be scrambled for float values.
INT32 dataType; // Specifies data type: float=0, fract32=1, int=2
void * subCanvasPtr; // Points to the Subcanvas module to control
} ModuleSubcanvasArraySetClass; Variables
Properties
Name | Type | Usage | isHidden | Default Value | Range | Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
setBehavior | int | parameter | 0 | 1 | Unrestricted | |
startIndex | int | parameter | 0 | 0 | Unrestricted | |
step | int | parameter | 0 | 1 | Unrestricted | |
outOfBoundsIndex | int | state | 0 | 0 | Unrestricted | |
enableRangeCheck | int | parameter | 0 | 0 | 0:1 | |
errorStatus | int | state | 0 | 0 | Unrestricted | |
objectHandle | uint | parameter | 1 | 0 | Unrestricted | |
targetClassId | uint | parameter | 1 | 0 | Unrestricted | |
arrayLength | int | parameter | 1 | 0 | Unrestricted | |
mask | uint | derived | 1 | 0 | Unrestricted | |
minValue | int | parameter | 1 | -100 | Unrestricted | |
maxValue | int | parameter | 1 | 100 | Unrestricted | |
dataType | int | parameter | 1 | 0 | Unrestricted | |
subCanvasPtr | void * | parameter | 1 |
| Unrestricted |
Pins
Input Pins
Enable Pin (optional) | |
|---|---|
Name | enable |
Description | parameter value |
Data type | int |
Channel range | 1 |
Block size range | 1 |
Sample rate range | Unrestricted |
Complex support | Real |
Value Pin | |
|---|---|
Name | value |
Description | values to set |
Data type | {float, int, fract32} |
Channel range | Unrestricted |
Block size range | Unrestricted |
Sample rate range | Unrestricted |
Complex support | Real |
Matlab Usage
function M = subcanvas_array_set_module(NAME, SUBCANVAS_NAME, MODVAR, ENABLE_PIN, EXECUTION_ORDER)
% M = subcanvas_array_set_module(NAME, SUBCANVAS_NAME, MODVAR, ENABLE_PIN, EXECUTION_ORDER)
% ArraySet module which works with the Subcanvas module. This module sets
% internal variables within the Subcanvas. It works with scalar and array
% variables and sets a single value. Arguments:
% NAME - name of the module.
% SUBCANVAS_NAME - name of the Subcanvas module that it is paired with.
% MODVAR - specifies the module and variable name using the form:
% 'MOD.VAR' where MOD is the module name and VAR is the
% variable name. You can also specify internal subsystems using
% 'SUBSYS.MOD.VAR'. The variable being written to must be an array.
% ENABLE_PIN - Boolean which adds an optional enable pin to the module.
% By default, ENABLE_PIN = 0.
% EXECUTION_ORDER - Determines when the ArraySet module executes relative
% to the module it is controlling. Allowable values are:
% 'undefined' - the default. The execution order is set
% by the routing algorithm and can occur before
% or after the module it is controlling.
% 'before' - forces ArraySet to execute before the module it
% is controlling.
% 'after' - forces ArraySet to execute after the module it
% is controlling.
% When using 'before' and 'after' you could get a build error
% indicating that no more modules can execute or there is a
% circular dependency.
%
% The information for the data type and array size is taken from the JSON file
% for the Subcanvas module.